Risk Governance
The Board of Directors has an overall responsibility for the governance of risks. The Audit and Risk Committee (ARC) assisted the Board of Directors in the oversight of risk management system, including the review of TSMC’s enterprise risk management (ERM) framework and process for the identification and management of risks and reports to the Board of Directors on material matters, findings and recommendations pertaining to risk management.
Risk Management Policy approved by the Board of Directors affirms TSMC’s commitment for mature and effective risk management system and culture in assisting management in making informed business decisions, by integrating and managing all potential risks to provide assurance that TSMC’s risks are known and within risk appetite and tolerance.

Risk Management Policy
The Audit and Risk Committees supports the Board of Directors in its oversight of risk management.
At the management level, it is supported by the various committees including risk management steering committee chaired by senior vice president of information technology and materials management and risk management, risk management executive council chaired by director of risk management division, risk management taskforces lead by risk management champions, supported by risk management division.
As part of the annual review of the risk management system, the key risks and mitigation efforts were reviewed by the Audit and Risk Committee at least twice a year on 5th February 2024 and to be reviewed on 12th August 2024.

Risk Management Organizations
TSMC’s risk management process is adopted with close reference to ISO31000:2018 Risk Management System and The Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO)’s Enterprise Risk Management - Integrated Framework. To support the achievement of corporate visions and business objectives, a proactive and robust risk management system is maintained to safeguard the interests of TSMC and our stakeholders. Resources are prioritized to focus on enterprise growth and strategy to effectively capitalize on opportunities and minimize the potential impact of threats, leading to value creation.
Enterprise Risk Management Framework and Procedure
TSMC’s enterprise risk management (ERM) framework is a systematic approach to effectively implement and continuously improve risk management system.
The Risk Management Division, working in conjunction with functional departments/divisions, supports management in applying the ERM framework to ensure risks across TSMC are assessed and adequately mitigated.
ERM framework outlines the risk governance structure, risk management process and tools in the identification, assessment, response, monitor and review of identified risks.
ERM implementation will be supported by an integrated risk management IT system and augmented with the establishment of Risk Management Academy focusing on building competencies and awareness in fostering a risk-aware mindset and culture.

Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) Framework and Procedure
Risk Appetite and Risk Management Scope
TSMC has defined its risk appetite statements, which outline the nature and extent of the risks which TSMC is willing to take in pursuit of its business goals. These risk appetite statements are:
- Strategic Risks: Risk taken should be carefully evaluated, commensurate with rewards and be in line with the Company’s strategic, investment, financial and corporate objectives.
- Operational Risks: Risk considerations are embedded into business operations and managed within the risk tolerance (risk indicators) of the divisions, functions and Company.
- Financial Risks: TSMC will not invest or participate in any business activities that exceeds our risk tolerance.
- Environmental, Safety and Health (ESH) & Compliance Risks: TSMC does not condone safety related breaches or lapses, non-compliance with laws and regulations, as well as acts such as fraud, bribery and corruption.
Adopting the five-step risk management process and risk rating matrix incorporating TSMC’s risk appetite, the risk assessments are performed by key functional units, to prioritize the identified risks and form the enterprise-level risk map and mitigation plans that are presented to the Audit and Risk Committee. This process is supported by ongoing education and awareness efforts in fostering a risk-aware culture and building risk competencies. TSMC recognizes that its systems and processes provide reasonable but not absolute assurance and hence the Company continually works to improve to ensure that its ability to manage and respond to risks and opportunities remain relevant and effective.
The scope of TSMC’s Risk Management encompasses, but is not limited to the following listed risk items:
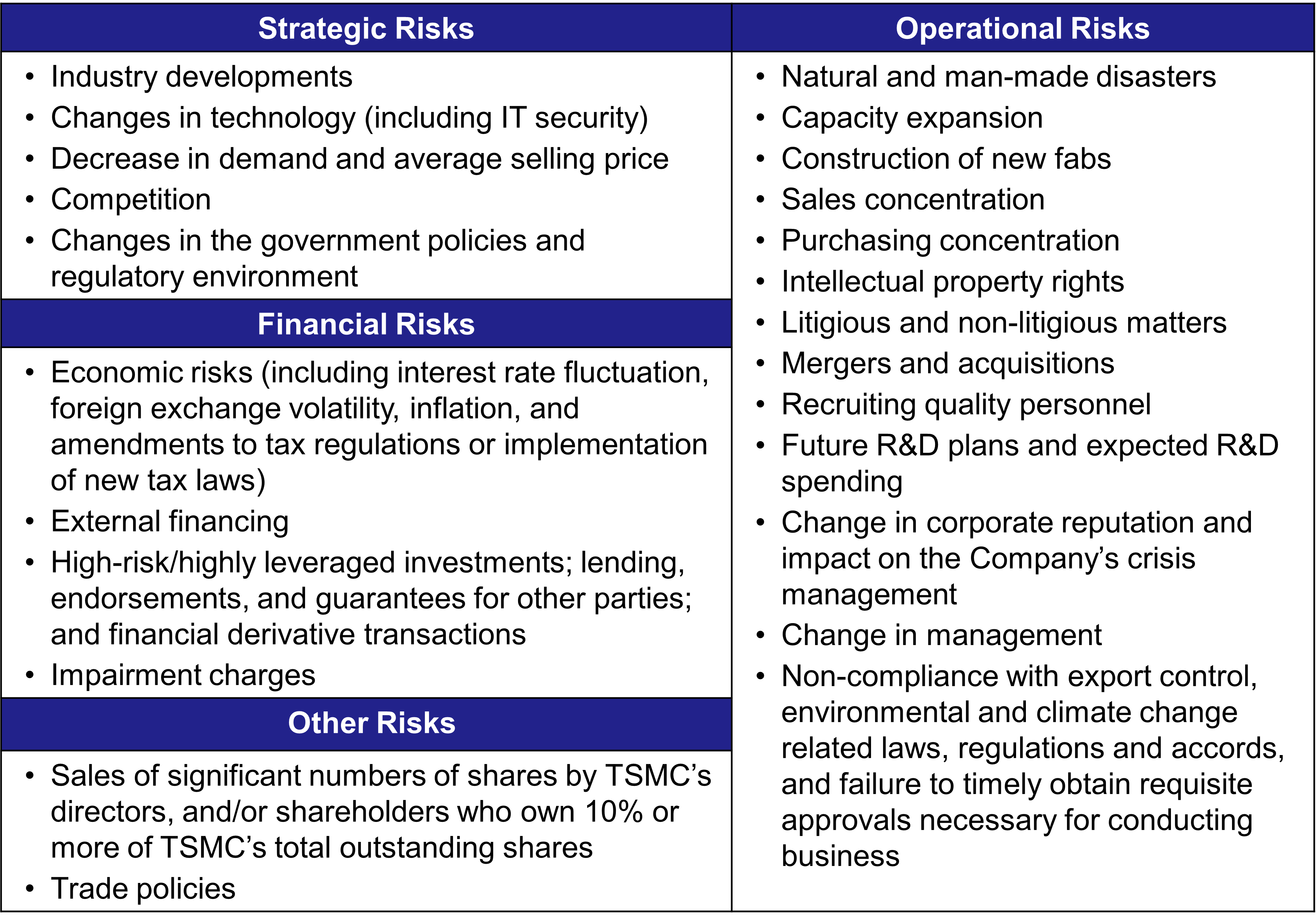
Focused Risk Evaluation and Review
Sensitivity Analysis and Stress Testing
TSMC performs sensitivity analysis and stress testing on financial risks and non-financial risks to validate its business resilience and strategically adapt to events that may have a material impact, including but not limited to:
- Market risk
- Credit risk
- Liquidity and solvency risk
- Gross margin sensitivity from change of foreign exchange and Utilization
- Overseas operation risk
- Financial impact from earthquake and power dip
Emerging Risk
Recognizing the importance of the analysis of global and emerging risks on TSMC’s corporate strategy, TSMC continues to scan our environment for risks that could have potential on our long-term sustainability.
TSMC’s top emerging risks are:
- Complexity in cyber landscape giving rise to sophisticated cyber threats: The adoption of new technologies such as AI and quantum computing increases cybersecurity risks, which is further exacerbated by cyber espionage. The semiconductor ecosystem, including suppliers and customers, is also at risk of cyberattacks, which could potentially have a major impact on the supply chain resulting to TSMC’s business interruption, loss of business opportunities, reputational impact, etc. Mitigating actions include but not limited to multi-layered defense, continuous simulation exercises, and supply chain security management.
- De-globalisation leading to Polarization of High-Tech Industry: National security is expected to be a growing concern and top priority of major countries that had deployed strategic actions to secure semiconductor self-sufficiency and localization of supply chains. This multi-polarization effect of the high-tech industry is weakening globalization and restricting the free flow of goods and technology for geopolitical gain. TSMC’s business might be faced with impact arising from weaken operational efficiency and resilience, elevated cost, loss of business opportunity, etc. Mitigating actions include but are not limited to risk-based strategic investment planning, localization and optimization of key operation resources, and enhancement of business continuity management.
- Climate Transition Action Failure: Climate inaction is one of the major threats to the world. Ineffective response to the changes related to the transition to a net-zero world poses risks to TSMC’s operations, value chain and markets, despite deploying strategies to address climate risks and opportunities. Mitigating actions include implementing plans targeting RE100 / net zero emission, and collaborating with external parties and authorities.
Risk Review
TSMC conducts internal and external audits of the risk management framework and process periodically, to identify opportunities to improve the effectiveness of risk management and its processes.
Information Security Risk Management
Information Security and Proprietary Information Protection are TSMC’s commitments to customers, shareholders, and business partners. TSMC established information security requirements, standards, and practices to enhance the Company’s management system and technology continuously, setting multi-layer defenses of information security. TSMC regularly performs risk assessments and implements comprehensive risk controls to achieve TSMC’s goals of information security management.
2023 Accomplishments and Key Enhancements in 2024
Risk Management Initiatives implemented in 2023 & key enhancements in 2024, reported to the Audit and Risk Committee, are summarized below:



